数据结构-图
本文介绍数据结构中图的概念,图的邻居矩阵表示、邻接表表示、Java 表示图的经典模板,以及常见用图的场景
# 数据结构-图
# 图的概念
图是一种非线性表数据结构,类似于树,但图的节点之间可以任意连接,结构更加复杂
图的关键词:
- 顶点:图的节点一般称为顶点
- 边:顶点间互相连接的关系,根据边是否有方向,分为有向和无向
- 权:边的权重或长度
- 度:与顶点相连接的边的数量,根据边的方向,分为入度和出度
图的分类
- 按边有没有方向:有向图 / 无向图
- 按边有没有权值:带权图 / 无权图
# 图的表示方式
# 邻接矩阵
假设每个顶点都有唯一的序号,可以使用矩阵来表示图
矩阵 A 的 $A[i][j]$ 位置表示节点 i 到 节点 j 是否有边,其值代表边的权
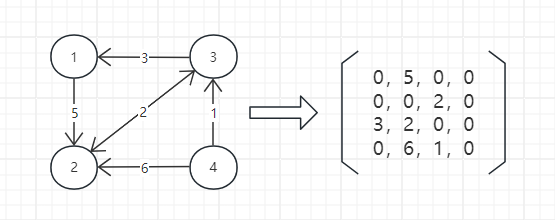
邻接矩阵可以表示有向和无向图
邻接矩阵存储方式简单,方便计算,但是当边比较稀疏时,空间浪费严重
# 邻接表
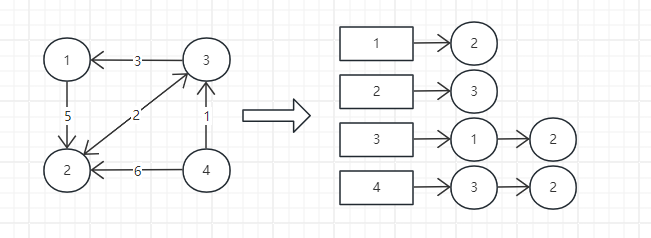
邻接表和散列表有些类似,每个顶点对应一条链表,链表中的节点是与该顶点相连接的其他顶点
邻接表也是可以表示有向和无向图
邻接表空间占用较少,但是计算时比较耗时,比如查找两顶点之间是否有连接,需要遍历链表
当然,在实际开发中可以使用其他高效的查找结构来代替链表,如有序数组、二叉查找树、散列表等
# Java 表示图的经典模板
图
public class Graph {
/**
* 序号和点 map
*/
public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 边集
*/
public HashSet<Edge> edges = new HashSet<>();
}
顶点
public class Node {
public int value;
/**
* 入度
*/
public int in = 0;
/**
* 出度
*/
public int out = 0;
public ArrayList<Node> nexts = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<>();
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
边
public class Edge {
public int weight;
/**
* 起点
*/
public Node from;
/**
* 终点
*/
public Node to;
public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}
示例:二维数组表示的有向图,转为上面的 Graph。此二维数组每个子数组是 $[边的权值,from 点序号,to 点序号]$
public static Graph createGraph(Integer[][] matrix) {
Graph graph = new Graph();
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
Integer edgeWt = matrix[i][0];
Integer fromVal = matrix[i][1];
Integer toVal = matrix[i][2];
if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(fromVal)) {
graph.nodes.put(fromVal, new Node(fromVal));
}
if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(toVal)) {
graph.nodes.put(toVal, new Node(toVal));
}
Node from = graph.nodes.get(fromVal);
Node to = graph.nodes.get(toVal);
Edge edge = new Edge(edgeWt, from, to);
graph.edges.add(edge);
from.edges.add(edge);
from.out++;
to.in++;
from.nexts.add(to);
}
return graph;
}
# 图的遍历
# 宽度优先遍历
宽度优先靠队列
遍历队列,遍历当前点的 nexts,每个没有被处理过的 next 都入队列
HashSet 保证不重复处理
public static void bfs(Node node) {
Set<Node> set = new HashSet<>();
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
set.add(node);
queue.offer(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node curr = queue.poll();
// 模拟处理
System.out.println(curr.value);
// ...
for (Node next : curr.nexts) {
if (!set.contains(next)) {
set.add(next);
queue.offer(next);
}
}
}
}
# 深度优先遍历
深度优先要用栈
每次弹出点,遍历当前点的 nexts,有一个 next 没有被处理过的,就压入当前点和该 next 并跳出 nexts 的遍历
HashSet 保证不重复处理
public static void dfs(Node node) {
Set<Node> set = new HashSet<>();
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
set.add(node);
stack.push(node);
// 模拟处理
System.out.println(node.value);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node curr = stack.pop();
for (Node next : curr.nexts) {
if (!set.contains(next)) {
stack.push(curr);
stack.push(next);
set.add(next);
// 模拟处理
System.out.println(next.value);
// ...
break;
}
}
}
}
# 常见用图的场景
图适合用来表达复杂的连接关系,在实际生活中,图有着广泛的使用空间
- 编程依赖关系:Maven 的依赖、项目的顺序编译等依赖图的拓扑排序算法
- 社交关系图谱:各类社交软件的好友关系、关注等功能
- 地图:利用图的路径相关算法提供最优路径推荐
- 图数据库:超大图、大量图计算,需要靠专业的图数据库,如 Neo4j
Comment here, be cool~
Loading
